What is the Difference Between a Wet and Dry Chemical Fire Extinguishing Agent?
Advances in fire protection technology have resulted in the development of fire extinguishing agents that are custom designed to suppress different types of fires based on the fuel type that is being consumed by the fire. Further, the Fire Triangle illustrates the three elements (heat, fuel, and oxygen) a fire needs to ignite and continue to burn, and different fire extinguishing agents interrupt the triangle in different ways to suppress the fire.
A wet chemical fire extinguishing agent is a liquid substance that extinguishes a fire by cooling or removing the heat and prevents the fire from reigniting by creating a barrier between the oxygen and fuel elements. A dry chemical fire extinguishing agent is a powdery substance that extinguishes a fire by smothering it and interrupting the chemical reaction by creating a barrier the fuel and oxygen.
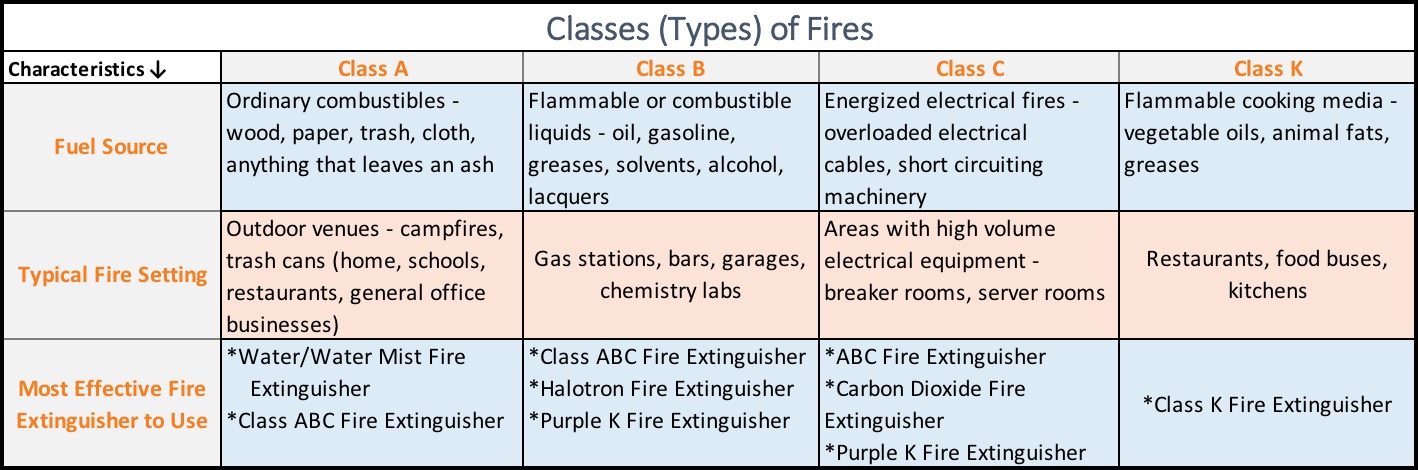
Wet chemical fire extinguishing agents include a blend of potassium acetate and potassium citrate and are used on Class K fires. Class K fires involve flammable cooking media such as vegetable oils, animal fats, and greases. Therefore, this type of fire extinguisher and agent is typically used in restaurants, kitchens, and food busses. The liquid chemical, upon contact with the cooking media, reacts and produces a foam to cool and also prevent reigniting.
Dry chemical fire extinguishing agents include sodium bicarbonate, potassium bicarbonate, and monoammonium phosphate and are used to combat Class A, B, and C fires. Class A fires involve ordinary combustibles such as wood, paper, cloth, and trash. Class B fires involve inflammable or combustible liquids such as oil, gasoline, greases, solvents, alcohol, and lacquers. Class C fires involve energized electrical fires that can occur from overloaded electrical circuitry and cables, and short-circuiting in certain equipment and machines.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Wet and Dry Chemical Fire Extinguishing Agents?
Wet Chemical Advantages
- This extinguishing agent is the best choice for use on kitchen fires because of the duel mechanisms to disrupt the Fire Triangle. It also is effective in preventing the fire from reigniting.
- The fire extinguishers that discharge the wet chemical do so with a lower pressure so as not to risk splattering the burning oil or grease which could spread the fire to other locations.
Wet Chemical Disadvantages
- The wet chemical suppression systems that are built into commercial kitchens require a significantly larger amount of space for installation and the associated construction costs.
Dry Chemical Advantages
- The most common dry chemical fire extinguisher is the ABC Dry Chemical. This one extinguisher is effective for use on three types (fuel source) of fires – Class A, B, and C.
- The dry chemical can be used in areas where wet chemical would cause significant damage, such as electronics.
- A dry chemical suppression system will require less storage space than a wet suppression system.
Dry Chemical Disadvantages
- The agents used are corrosive and must be scrubbed off surfaces after a fire.
- If the dry chemical is used in a suppression system, it requires being refilled and recharged after each time the system is activated.
|
· Note: Wet chemical suppression systems are required to comply with NFPA 17A (Standard for Wet Chemical Extinguishing Systems) and NFPA 96 (Standard for Ventilation Control and Fire Protection for Commercial Cooking Operations). · Note: Dry chemical suppression systems are required to comply with NFPA 17 (Standard for Dry Chemical Extinguishing Systems) and NFPA 33 (Standard for Spray Application to Safely Use on Flammable and Combustible Materials) |
What are the other types of fire extinguishing agents?
In addition to the wet and dry chemical fire extinguishing agents listed previously, other types of extinguishing agents include:
Click on the images below to view a helpful chart on the different characteristics of the various Classes of Fires and a listing of the various types of fire extinguishers and agents used to combat the different Classes of Fires.